Kinetic Energy Relative to Center of Mass
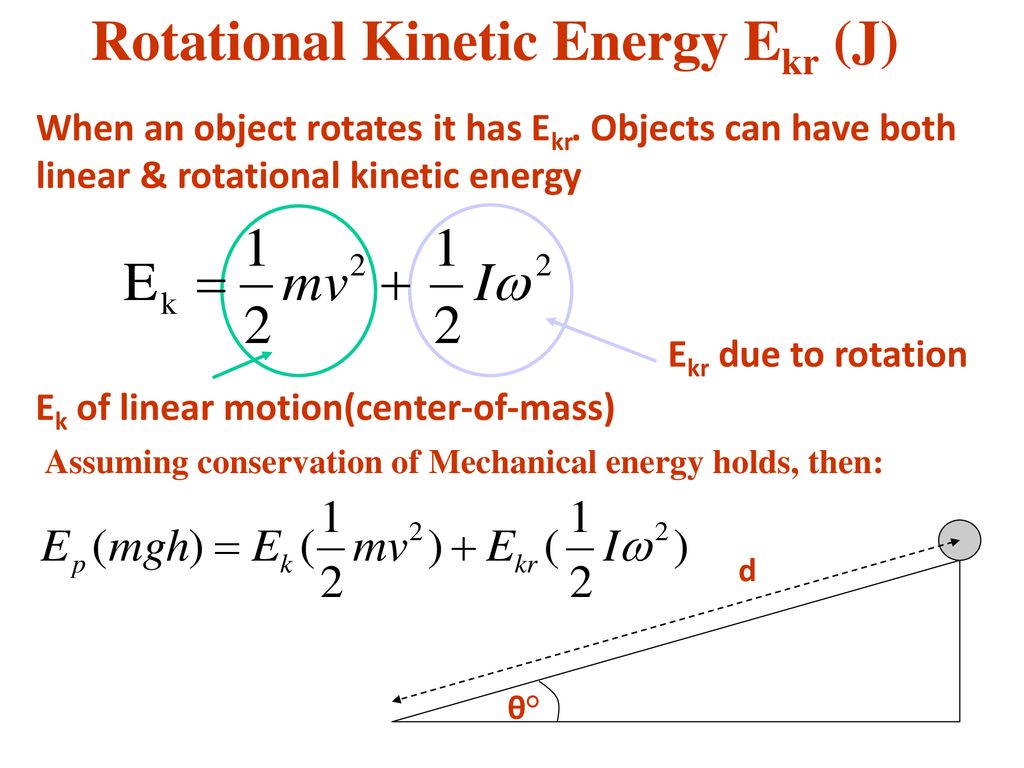
Total kinetic energy of two particle system is the sum of kinetic energy of system with respect to the centre of mass and kinetic energy of the centre of mass. If an object is rotating as well as its center of mass is moving in a straight line then the total kinetic energy is given by the sum of rotational and translational kinetic energies.

Homework And Exercises Total Kinetic Energy Of Two Particle System Physics Stack Exchange
The center of mass of a rod of course is in the center of the rod at a distance L 2.
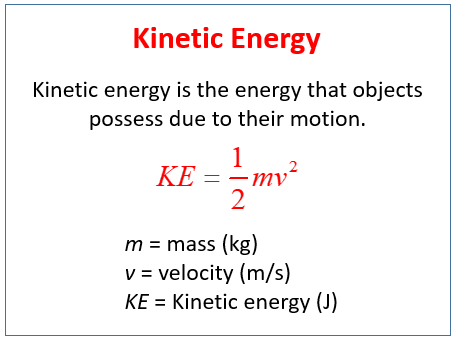
. What is the speed of the center of mass. The kinetic energy relative to the center of mass is 80 J. 1 the motion of the center of mass translational motion 2 the motion of the object relative to the center of mass relative motion.
A rotating object has kinetic energy because all particles in the object are in motion. Starting from rest you pull the string with a constant force of 13N along a nearly frictionless surface. And substituting back in and rearranging gives.
V cm r_ cm 1 M P n i1 m r_ i I In the Lab frame total momentum p tot. The answer is that the total kinetic energy of a system relative to an arbitrary inertial frame according to Newtonian physics is the sum of the total kinetic energy of the system relative to the center of mass frame plus a term. One way to calculate K rel is to calculate the velocity of each particle relative to the center of mass by subtracting the centerof-mass velocity from the particles actual velocity to get the particles velocity relative to the center of mass then calculating the corresponding kinetic energy then adding up the three relative kinetic energies.
And I believe the kinetic energy in the center of mass frame is given by. Since even if the velocity is said to be zero it is still relative to an observer. The total kinetic energy is the sum of the kinetic energy of each particle in the system.
At the instant when the center of the disk has moved a distance 013m your hand has moved a distance 034m. Its the total kinetic energy of the two blocks when viewed in the reference frame of the center of mass. Consider a pure rotation of a solid object.
Let us just see whether it works for the rod. Modeling the system as a point particle with all of its mass concentrated at its center of mass is called translational kinetic energy. The kinetic energy due to rotation is called rotational kinetic energy.
In the CAD the range of internal energies acquired by protonated mole- experiment an initial kinetic energy spread of 7 eV hELm cules undergoing collisional excitation is largeq for surface is dramatically attenuated when laboratory energy is converted collisions SID13 eV than for target gas collisions CAD 100 into center-of-mass energy. On the other hand the average kinetic energy of the individual. At this instant what is the speed of the center of mass of the disk.
The total kinetic energy of the system is equal to the sum of the kinetic energy of a particle of mass M moving with the velocity of the center of mass and the kinetic energy of the motion of the individual particles relative to the center of mass. 1 2 M v c m 2. Do not just use K 12 m v2 gets the wrong answer.
P tot P n i1 mi r_ i Mv cm Hence the total momentum of a system in the Lab frame is equivalent to that of a single particle having a mass M. R cm 1 M P n i1 m r i where M P n i1 mi I The velocity of the CM. Linear ½ I ω 2 ½ m v 2.
The center-of-mass energy of a system of particles is the energy measured in the center-of-mass reference frame see below. Since is the speed of center of mass. The original kinetic energy is.
Kinetic energy of m₁ with respect to the centre of mass is. The units of moment of inertia are kg m2. If the total angular momentum of the molecule is 105 10-34 J s then a determine the angular velocity relative to the center of mass b determine the kinetic energy relative to the center of mass and c find the value for the center-of-mass velocity that would make the kinetic energy of the center of mass equal to the kinetic energy relative to the center of mass.
K trans 1 2 Mv2 cm p2 2M 15 If you imagine that the center of mass is at rest this is called the center of mass reference frame then. A group of particles of total mass 36 kg has a total kinetic energy of 308 J. E 1 c m 1 2 m 1 m 2 v 1 2 m 1 m 2 2 1 2 m 1 m 2 2 m 1 m 2 2 v 1 2 2.
However there is a much simpler. T c m 1 2 m i v i v c m 2 1 2 m i v i 2 2 v i v c m v c m 2 1 2 m i v i 2 m i v i v c m 1 2 m i v c m 2. For example when a spring uncompresses and accelerates a mass as in the configuration of FigB2 work is performed on the mass by the spring and we say that the potential energy of the spring is converted to kinetic energy of the mass.
Kinetic Energy of a Mass. This implies that the kinetic energy of a center of mass is also relative to the observers velocity compared to the observed body. Therefore we should find that ML2 3 ML2 12 ML 22.
ANSWER IS NOT 80 12 34 v2 v is NOT 2169. Translational Kinetic Energy m I v Moment of inertia is the rotational equivalent of mass. The kinetic energy relative to the center of mass is 87J.
T 1 2 m i v i 2. Answer 1 of 5. For an axis through one end the moment of inertia should be ML2 3 for we calculated that.
632 Velocity in the Centre of Mass frame I The position of the centre of mass is given by. Kinetic energy is energy associated with motion. Also called internal kinetic energy because its the kinetic energy of the motion of the internal components of the system not of the motion of the systems center of mass.
A group of particles of total mass 34 kg has a total kinetic energy of 399 J. We need to find the speed of center of mass. This energy constitutes all the energy that is available to create new particles or to explore the internal structure of particles since the energy of the motion of the center of mass itself stays with the center of mass.
The kinetic energy relative to the center of mass is K 81 J. We know that the total kinetic energy is equal to the sum of rotational kinetic energy and the rotational kinetic energy. The kinetic energy of the center of mass ie.
What is the speed of the center of mass. Or which can be conveniently rewritten as Breaking up the motion Break up the motion into two parts.
Rotational Kinetic Energy Ekr J Ppt Download

Question Video Comparing The Kinetic Energies Of Objects Nagwa

Kinetic Energy Examples Video Lessons Examples Step By Step Solutions
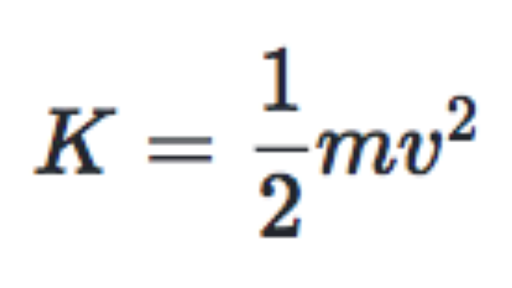
No comments for "Kinetic Energy Relative to Center of Mass"
Post a Comment